Ayurveda is India's traditional, natural system of medicine that has been practiced for more than 5,000 years. Ayurveda is a Sanskrit word that literally translated means "science of life" or "practices of longevity." Ayurveda was the system of health care conceived and developed by the seers (rishis) and natural scientists through centuries of observations, experiments, discussions, and meditations. For several thousand years their teachings were passed on orally from teacher to student; about the fifth to sixth century BC, elaborately detailed texts were written in Sanskrit, the ancient language of India. For many years Ayurveda flourished and was used by rich and poor alike in India and Southeast Asia.
Manuscript page from Atharva-Veda, earliest Indian text (approx. 1500 BC) with much medical information, one of several Vedas (meaning "knowledge"), upon which Ayurvedic medical practice is based on. Ayurvedic manuals were written by Charaka, Sushruta, and Vagbhata that give detailed descriptions of the various practices. Charaka listed 500 hundred remedies and Sushruta over 700 vegetable medicines. Ayurveda emphasizes prevention of disease, rejuvenation of our body systems, and extension of life span. The profound premise and promise of Ayurveda is that through certain practices, not only can we prevent heart disease and make our headaches go away, but we can also better understand ourselves and the world around us, live a long healthy life in balance and harmony, achieve our fullest potential, and express our true inner nature on a daily basis. Ayurveda provides an integrated approach to preventing and treating illness through lifestyle interventions and natural therapies. It is based on the view that the elements, forces, and principles that comprise all of nature - and that holds it together and make it function - are also seen in human beings. In Ayurveda, the mind (or consciousness) and the body (or physical mass) not only influence each other - they are each other. Together they form the mind-body. The universal consciousness is an intelligent, aware ocean of energy that gives rise to the physical world we perceive through our five senses. Ayurvedic philosophy and practices link us to every aspect of ourselves and remind us that we are in union with every aspect of nature, each other, and the entire universe.
There can be no mental health without physical health, and vice versa. In Ayurveda, symptoms and diseases that could be categorized as mental thoughts or feelings are just as important as symptoms and diseases of the physical body. Both are due to imbalances within a person, and both are treated by restoring the natural balance mentally and physically. In Ayurveda your whole life and lifestyle must be in harmony before you can enjoy true well being. Lifestyle interventions are a major Ayurvedic preventive and therapeutic approach.
In India, Ayurvedic practitioners receive state-recognized, institutionalized training in parallel to their physician counterparts. The research base is growing concerning the physiological effects of meditative techniques and yoga postures in Indian medical literature and Western psychological literature. Published studies have documented reductions in cardiovascular disease risk factors, including blood pressure, cholesterol, and reaction to stress, in individuals who practice Ayurvedic methods.
Laboratory and clinical studies on Ayurvedic herbal preparations and other therapies have shown them to have a range of potentially beneficial effects for preventing and treating certain cancers, treating infectious disease, treating diabetes, promoting health, and treating aging. Mechanisms underlying these effects may include free-radical scavenging effects, immune system modulation, brain neurotransmitter modulation, and hormonal effects

It is considered as one among the poorvakarmas (preparatory procedures). It implies synchronized massage to the whole body or local body parts as per the condition of disease. It is one among the most common and effective therapy in Ayurvedic medicine. Useful in nerve disorders, aches and stiffness. It is usually done for 40 to 60 minutes depending upon the need.

It is a procedure of retaining warm medicated oil(thailam) in a cap like structure fitted on head. Normally this procedure will be done for 35-50 min for a time period of 7 days maximum. This is considered as one of the greatest treatment for head.

It is considered as one among the poorvakarmas (preparatory procedures). Usually the time period of Swedanam is, till the patient gets proper sweating all over the body. It gives a feeling of lightness, it is good for skin, helps to reduce the fats collected even on extremities.

It is a type of swedana (sudation)in which the patient is made to sit in a tub containing medicated liquid for a certain period of time.It is very helpful in treating uro genital,gynaec,anorectal diseases etc

This is also a type of swedana(sudation) in which steam of medicated milk is made to be exposed to face for a certain time.It is effective in treating facial palsy,dribbling of saliva,strengthening of facial muscles etc

It the oral consumption of Sneham (oleos substances). Generally it is done with Ghrutham (medicated ghee). It is considered as an important preparatory procedure for the Panchakarma therapies (purification therapies) as well as it is considered even as a main procedure in treating severe disorders like infertility, psychiatric diseases etc.
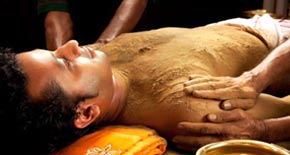
This procedure is done here with medicated powder (choornam) mixed in mild hot thailam, in which this combination of medicines will be rubbed on the body surface with moderate pressure in prathilomagathi (opposite direction of normal massage). It is very useful in weight reduction.

It is the nasal administration of medications. It is a very effective therapy for all systemic disorders especially those related with the head and neck. It is a proved effective therapy for psychiatric disorders.